Scabies Treatment Comparison Tool
Recommended Treatment Based on Your Profile
Effectiveness:
Side Effects:
Cost:
All Treatment Options
TL;DR
- Eurax (crotamiton) is a 10% cream that both relieves itch and kills scabies mites, but it works slower than permethrin.
- Permethrin 5% cream is the most effective single‑dose option for most people.
- Oral ivermectin is useful for severe or crusted scabies and for patients who can’t use creams.
- Benzyl benzoate and sulfur ointment are cheap, but they irritate skin and need multiple applications.
- Choose based on age, skin sensitivity, severity, and whether you need a single‑dose or multi‑dose regimen.
Scabies infests millions of people each year, causing relentless itching and a rash that spreads quickly. While over‑the‑counter ointments exist, many patients wonder if Eurax is the right choice or if another drug would work better. This guide compares Eurax (crotamiton) side‑by‑side with the most common alternatives, breaks down how each works, and helps you pick the safest, most effective option for your situation.
What is Eurax (Crotamiton)?
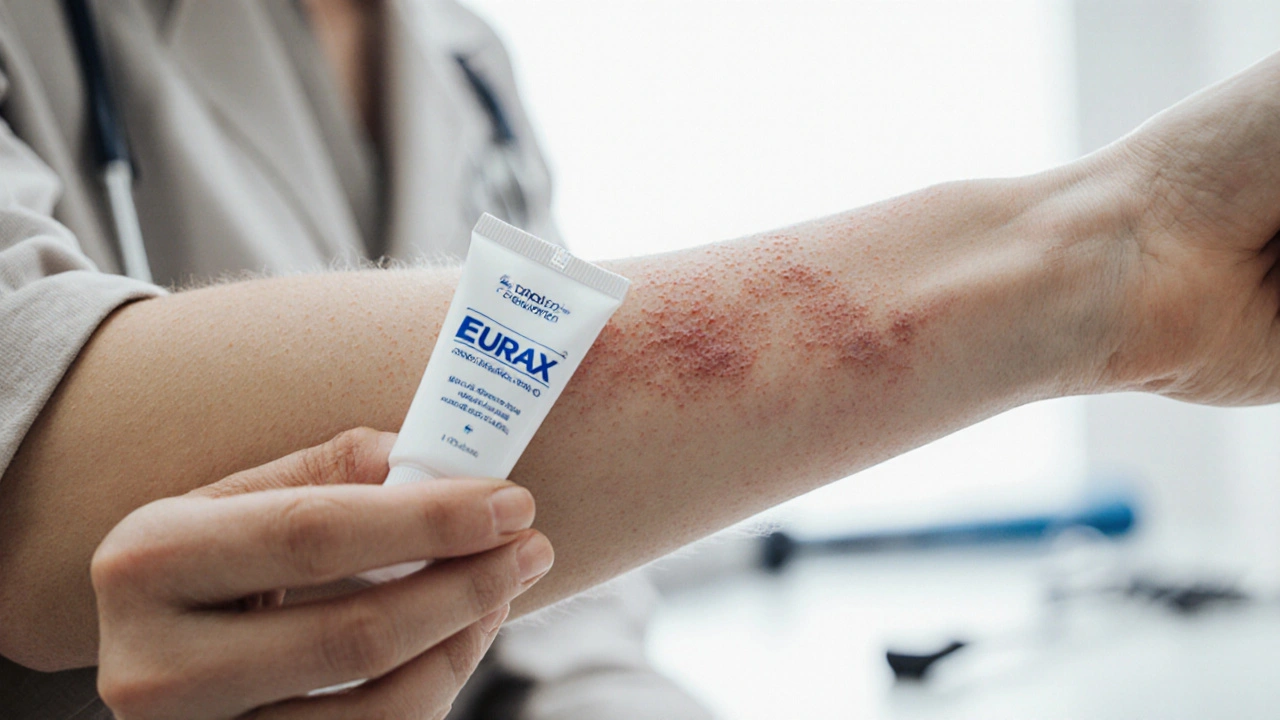
When treating scabies, Eurax is a topical cream that contains 10% crotamiton, an antipruritic and acaricidal agent approved in many countries for both scabies and lice. It was first launched in the early 1990s and quickly became popular because it offers two benefits in one product: it eases itching and gradually kills the mite.
Key attributes of Eurax:
- Formulation: 10% crotamiton cream, applied topically.
- Indication: Scabies infestations (adults and children over 2years) and head lice.
- Typical regimen: Apply once daily for 24hours, repeat for 3‑5days.
- Efficacy: Clinical studies show 70‑80% cure rates after a full course; itch relief appears within 24‑48hours.
- Side effects: Mild skin irritation or burning in ~5% of users; rare allergic reactions.
- Cost: Moderate; in the U.S. a 30g tube ranges $15‑$20.
Because Eurax works slower than some newer agents, doctors often reserve it for patients who can’t tolerate permethrin or who need an added antipruritic effect.
How Eurax Works
Crotamiton disrupts the nervous system of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, leading to paralysis and death. At the same time, it blocks histamine release in human skin, which reduces the itch sensation. This dual action means patients feel better before the mites are fully eradicated, improving compliance.
In pharmacological terms, crotamiton binds to mite GABA receptors, causing hyperexcitation and eventual death. The compound has a low systemic absorption rate, making it safe for most skin types when used as directed.
Common Alternatives to Eurax
Below are the five most widely used scabies treatments that clinicians compare against Eurax. Each entry includes a brief definition with microdata markup, followed by its pros and cons.
Permethrin is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide formulated as a 5% cream, considered the first‑line therapy for scabies worldwide.
- Fast‑acting: kills >99% of mites after a single 8‑hour application.
- Safe for infants over 2months and for pregnant women.
- Minimal irritation; occasional tingling.
- Cost: $10‑$15 per tube (often covered by insurance).
Benzyl benzoate is a liquid lotion (usually 25% concentration) that acts as a neurotoxin for scabies mites.
- Very inexpensive; generic versions <$5 per bottle.
- Requires multiple applications (often 2‑3days apart).
- High irritation potential; strong odor.
- Not recommended for children under 2years.
Ivermectin is an oral antiparasitic that interferes with nerve transmission in mites, used for severe or crusted scabies.
- Dosage: 200µg/kg, taken as a single dose or repeated after 1‑2weeks.
- Effective for patients who cannot apply creams (e.g., limited mobility).
- Systemic side effects are rare but can include dizziness or nausea.
- Cost varies; generic tablets about $30‑$40 per course.
Sulfur ointment is a traditional treatment (5‑6% sulfur) that kills mites through a slow oxidizing action.
- Very cheap; over‑the‑counter for <$3 per tube.
- Requires nightly application for 3‑5days.
- Leaves a distinct yellowish residue and odor.
- Safe for infants and pregnant women.
Lindane is an organochlorine insecticide historically used for scabies but now restricted in many regions due to neurotoxicity concerns.
- High efficacy (single dose).
- Significant risk of seizures and skin irritation.
- Limited availability; many health agencies advise against use.
Side‑by‑Side Comparison
| Attribute | Eurax (Crotamiton) | Permethrin 5% | Benzyl benzoate 25% | Ivermectin (oral) | Sulfur ointment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | Cream (10%) | Cream (5%) | Lotion (25%) | Tablet (200µg/kg) | Ointment (5‑6% sulfur) |
| Typical regimen | Apply daily for 3‑5days | Apply once, leave for 8h | Apply, repeat 2‑3days | 1‑2 doses, 1‑2weeks apart | Nightly for 3‑5days |
| Cure rate | 70‑80% | >95% | ~85% | 90‑95% (severe cases) | ~80% |
| Itch relief | 24‑48h (antipruritic) | 48‑72h | 48‑72h | 72h+ | 72h+ |
| Skin irritation | Low (5%) | Very low | Moderate‑high | Rare | Low‑moderate (odor) |
| Cost (U.S.) | $15‑$20 | $10‑$15 | $5‑$8 | $30‑$40 | $2‑$4 |
| Age limits | ≥2years | ≥2months | ≥2years | ≥15kg (≈12years) | All ages |
How to Choose the Right Treatment
Deciding between Eurax and its alternatives depends on three practical factors: severity of infestation, patient age/skin sensitivity, and preference for single‑dose versus multi‑dose regimens. Use the quick‑decision guide below.
- Mild to moderate scabies in a child over 2years: Permethrin 5% cream is usually the best first‑line choice because it works fast and has minimal irritation.
- Older adult with sensitive skin who also suffers from intense itching: Eurax offers antipruritic relief while still clearing the mites, making it a comfortable option.
- Crusted (Norwegian) scabies or cases where creams cannot be applied: Oral ivermectin, often combined with a topical agent, provides systemic coverage.
- Very low budget and no strong skin reactions: Sulfur ointment or benzyl benzoate are cost‑effective, though they require patience.
- Concern about neurotoxic chemicals: Avoid lindane; modern guidelines advise safer alternatives.
Always complete the full course, even if symptoms improve early. Stopping treatment prematurely can let surviving mites repopulate, leading to relapse.
Applying Eurax Safely - Step‑by‑Step
- Clean the affected area with mild soap and warm water; pat dry.
- Apply a thin layer of Eurax cream over the entire body from the neck down (including under nails and folds).
- Leave the cream on for 24hours; do not wash off.
- After 24hours, wash the area gently and reapply if your doctor prescribed a 3‑day or 5‑day regimen.
- Wash all bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water (≥60°C) and dry on high heat to prevent reinfestation.
If you notice increasing redness, blistering, or a rash that spreads beyond typical scabies lesions, stop the product and seek medical advice-these could be signs of an allergic reaction.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use Eurax on infants?
Eurax is approved for children aged 2years and older. For younger infants, permethrin 5% cream is the safer first‑line option because it has a well‑established safety profile in babies as young as two months.
How long does it take for itching to stop?
Eurax’s antipruritic component usually eases itch within 24‑48hours, while the mite‑killing action may need 3‑5days of daily use. Permethrin often reduces itching a bit slower (48‑72hours) because it lacks a built‑in antipruritic.
Is a single dose of Eurax enough?
No. Clinical guidelines recommend applying Eurax once daily for at least three days, sometimes up to five, to ensure all life stages of the mite are eradicated.
Can I combine Eurax with another scabies medication?
Combining treatments is generally discouraged unless a healthcare provider advises it for severe cases. Mixing a topical cream with oral ivermectin can be done under supervision, but using two topicals together may increase skin irritation.
How do I prevent re‑infestation after treatment?
Wash all clothes, bedding, and towels in hot water and dry on high heat. Vacuum carpets and upholstered furniture, then discard the vacuum bag. Treat close contacts simultaneously, even if they show no symptoms, because scabies spreads easily.
Whether you opt for Eurax, permethrin, ivermectin, or a traditional remedy, the key is to follow the full regimen and address the environment. With the right choice, scabies is a short‑term inconvenience, not a lasting problem.

When you’re trying to decide between Eurax and the other options, start by looking at the two main factors: how quickly the medication knocks out the mites and how it treats the itching. Eurax’s dual action can be a real comfort for people with very sensitive skin because it soothes the itch while it works, even though the kill‑rate is a few points lower than permethrin. If you’re dealing with a mild infestation and you have a history of irritation from stronger creams, the slower onset may be a worthwhile trade‑off. On the other hand, for a severe case you’ll probably want the fastest‑acting agent, which points toward permethrin or oral ivermectin. Ultimately, match the drug to the patient’s age, skin tolerance and how fast you need relief.
Eurax is a joke you’re paying for a slow‑acting cream
Choosing a cheap, irritating formula when a highly effective, low‑risk alternative exists feels like neglecting basic patient safety. Permethrin clears the majority of mites in a single night, while Eurax drags its feet and still leaves a notable failure rate. If you can afford the marginally higher price of the proven cream, why settle for something that merely eases itch? The moral of the story is simple: prioritize efficacy over comfort when dealing with a contagious parasite.
The mechanism of crotamiton involves binding to the mite’s GABA receptors, causing uncontrolled neural firing that ultimately leads to paralysis and death. Simultaneously, it stabilizes human mast cells, which reduces histamine release and therefore the pruritus associated with scabies. Clinical trials have shown cure rates in the range of 70‑80 % after a full 3‑5 day course, which is respectable but still below the >99 % success of permethrin. In terms of systemic absorption, crotamiton remains largely topical, making it safe for most patients, including children over two years old. Side‑effects are generally mild, with occasional localized irritation reported in about five percent of users. Cost-wise, a 30 g tube runs roughly $15‑$20, positioning it in the mid‑range compared with other topical agents.
Honestly, I think the whole hype around permethrin is overblown – it’s not like it’s suer safe for everyone. Sure, it works fast, but the chemical can be harsh on very sensitve skin, and the cummunication from pharma makes us think it’s the only choice. Eurax offers a gentler alernative while still knockin out the mites in a reasonable time. People need to stop being so quick to dismiss anything that isn’t the #1 brand.
Oh, brilliant, let’s all jump on the permethrin bandwagon because it’s “fast‑acting”. As if speed is the only metric that matters when you’re also battling a nightmare of itching that can keep you up all night. Eurax might take a little longer, but at least it doesn’t leave you with a burning sensation that feels like a tiny fire on your skin. Some people actually prefer a slower, kinder approach over a chemical blitz.
While the content of this guide is helpful, the presentation suffers from several grammatical oversights. For instance, the phrase “fast‑acting and safe for most patients” should be punctuated with a comma before “and”. Moreover, the use of inconsistent tense in describing side‑effects can confuse readers. Precision in language mirrors precision in treatment, and both deserve careful attention.
Let me tell you, the drama of choosing a scabies cream is real! You’re faced with a decision that could turn your skin into a battlefield or a peaceful meadow. Eurax, with its soothing properties, feels like a gentle lullaby, while permethrin screams “I’m here to kill!” at the cost of that harsh sting. And don’t even get me started on the pungent odor of benzyl benzoate – it’s like a chemical warzone in your bathroom. In the end, the choice is yours, but remember: your skin will remember it forever.
What the pharma companies don’t want you to see is that the “highly effective” permethrin claims are part of a larger agenda to keep us dependent on pricey, patented solutions. By pushing a fast‑acting synthetic, they profit from repeat prescriptions and the fear they create about slower, older treatments like Eurax. The truth is hidden behind glossy marketing, and it’s up to us to question why we’re being sold a single‑dose miracle instead of a balanced, affordable option.
Let’s take a step back and look at the bigger picture. If you have sensitive skin or a child, Eurax’s gentle approach can be a real blessing, even if it takes a little longer. For a severe infestation, the rapid knock‑down of permethrin or oral ivermectin is often the safest bet. Think about your personal situation, weigh the pros and cons, and choose the therapy that aligns with both your comfort and the urgency of clearing the mites.
It is a fascinating exercise to compare a decade‑old 10 % crotamiton cream with today’s “world‑changing” scabicides, especially when the marketing copy promises both itch relief and mite eradication in a single product. First, let us acknowledge that Eurax does indeed soothe pruritus, which is a non‑trivial benefit for patients who spend nights scratching until their skin bleeds. Second, the efficacy data, hovering around 70‑80 % after a full course, implies that a non‑negligible fraction of infestations will require a second round of treatment or an adjunctive therapy. Third, the time‑to‑kill metric is slower than permethrin’s near‑instantaneous action, meaning that the itch may persist longer, potentially leading to secondary bacterial infection. Fourth, the safety profile is respectable; systemic absorption is minimal, and adverse reactions are limited to mild local irritation in roughly five percent of users. Fifth, the cost sits at $15‑$20 per tube, which is affordable for many but still higher than the cheapest benzyl benzoate alternatives. Sixth, the convenience factor must be considered – Eurax requires daily application for several days, whereas permethrin is a single‑dose regimen. Seventh, patient adherence tends to improve when the regimen is simple, making the single‑dose therapy attractive despite its higher efficacy. Eighth, for pediatric patients and those with very sensitive skin, the gentler nature of Eurax may outweigh the slower kill rate, as the risk of irritation from permethrin, albeit low, is not zero. Ninth, the practical reality is that many clinicians reserve Eurax for those who cannot tolerate permethrin or who have specific contraindications. Tenth, the broader public health implication is that faster‑acting treatments may reduce transmission more effectively in crowded settings. Eleventh, however, the over‑reliance on a single “gold‑standard” drug can foster resistance, a concern that is increasingly discussed in dermatology circles. Twelfth, thus having a viable alternative like Eurax in the therapeutic arsenal is arguably prudent. Thirteenth, the decision matrix ultimately hinges on individual patient factors: age, skin type, severity of infestation, and personal preference. Fourteenth, no single drug is universally superior, and the clinician’s role is to tailor therapy accordingly. Fifteenth, in the end, the choice between a slower, soothing cream and a rapid, potent agent is less about superiority and more about matching the right tool to the right job. Sixteenth, remember, the best treatment is the one the patient will actually use consistently, lest all the pharmacology in the world be wasted.
The balance of efficacy and comfort in scabies therapy is a delicate dance, and Eurax offers a softer step for those whose skin protests harsh chemicals.
We are, in essence, tiny ecosystems of microbes and human ambition, and the decision to sprinkle a chemical like permethrin across our skin is a profound statement about our mastery over nature. Yet, the very act of choosing a slower, more compassionate cream like Eurax speaks to a humility that many modern treatments lack.
From a pharmacokinetic perspective, the logarithmic decay of mite viability under crotamiton exposure suggests a sub‑optimal AUC compared to the exponential kill curve exhibited by pyrethroids, which technically renders Eurax a second‑line option in most evidence‑based algorithms.
While the data certainly highlight the superior rapidity of permethrin, let us not overlook the patient‑centered benefits of Eurax, especially in cases of heightened dermal sensitivity; a balanced approach, incorporating both efficacy and tolerability, may ultimately serve the broader community best.
Sounds like a solid plan-match the treatment to the individual's needs.
It’s amusing how the conversation swings from “Eurax is too slow” to “permethrin is a miracle drug,” as if we haven’t seen this pendulum swing in countless dermatology debates before. On one hand, the rapid knock‑down of mites by permethrin can be a lifesaver in outbreak settings, but on the other hand, the gentle, itch‑relieving properties of Eurax can make the difference between an overnight nightmare and a manageable recovery. So, perhaps the real wisdom lies not in crowning a single champion, but in recognizing that each medication has its own niche-a bit like assigning roles in a well‑orchestrated symphony. Ultimately, the clinician’s job is to listen to the patient’s concerns, assess the severity, and prescribe accordingly, all while keeping an eye on cost and accessibility. In short, no one‑size‑fits‑all; the best outcome comes from a tailored, patient‑first approach.
Don’t be fooled by the glossy ads-big pharma loves to push the “quick‑fix” creams while hiding the fact that they’re testing new chemicals on us every year 🚨💊. Stay informed, read the fine print, and consider the older, proven options that don’t come with secret side‑effects.